Physician-Powered AI Robot Revolutionizes Stroke Care Across the SEHA Network
Lit. No. LG-2025-001 600022226 | 5202025
May 2025 | Lyons Global®
Abstract
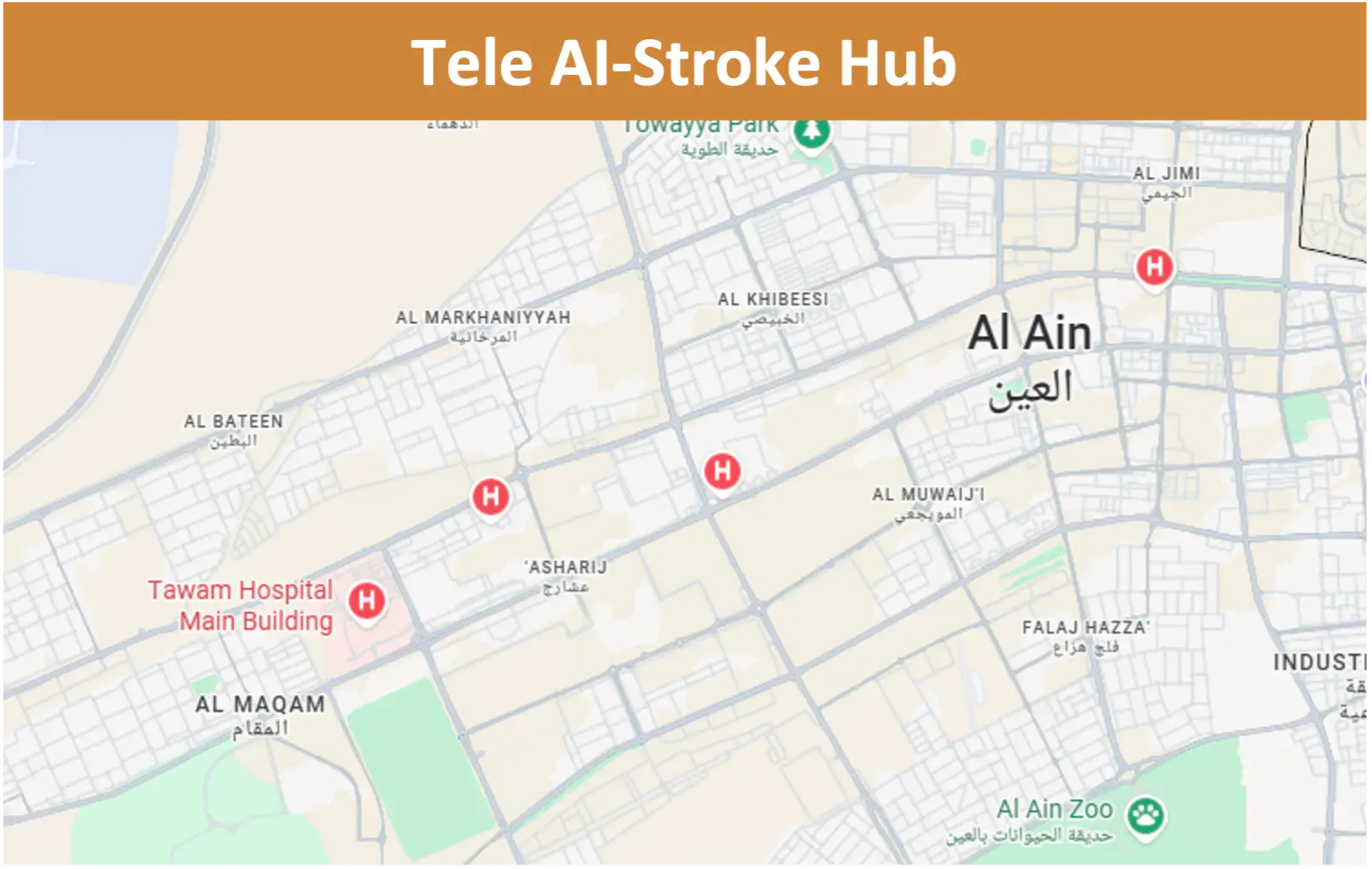
In early 2025, SEHA healthcare system launched the UAE’s first AI-powered Tele-Stroke Hub through its flagship hospitals—STMC and Al Tawam Hospital—utilizing the LEO360® Medical AI Robot. The program delivered transformational outcomes, including a 90% reduction in time-to-neurologist evaluation, 80% decrease in inter-hospital transfers, and a marked improvement in stroke response and diagnostic accuracy. This case study presents the clinical execution, results, and scalability of the LEO360®-based stroke model and introduces a new standard for remote neurological care in the region.
Introduction
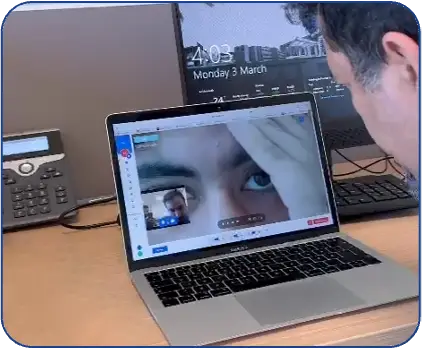
STMC and Al Tawam Hospital together manage nearly 430,000 patients annually. Despite their leading infrastructure, timely stroke specialist access—especially after hours—remained a critical gap. “Time is brain” and SEHA recognized the need for an always-available, AI-enhanced neurology response system. The answer was LEO360®: a physician-powered robotic solution with advanced imaging, real-time assessment capabilities, and seamless network integration.
Objective
- Deliver rapid neurologist access within 15 minutes for all suspected stroke patients
- Avoid unnecessary inter-hospital transfers
- Improve diagnostic accuracy and reduce misclassification of stroke mimics
- Optimize patient outcomes and enable real-time care decisions
AI-powered Tele-Stroke Hub with LEO360® Robot Implementation Highlights:
AI-powered Tele-Stroke Hub with LEO360® Robot Clinical Case Summaries:
|
Patient |
Hospital |
Robotic Consultation |
Outcome |
|
Patient A |
Al Tawam |
11 min |
AVM diagnosis in 11 minutes → stroke unit admission |
|
Patient B |
Al Tawam |
10 min |
Remote neurologist ruled out stroke; admitted for MRI and monitoring |
|
Patient C |
STMC |
10 min |
TIA vs hemiplegic migraine; unnecessary treatment avoided |
|
Patient D |
STMC |
11 min |
AVM detected early → long-term care path initiated |
|
Patient E |
STMC |
8 min |
NIHSS 13 stroke mimic identified; hemorrhage excluded |
|
Patient F |
STMC |
14 min |
Lacunar infarct confirmed; stroke risk mitigated |
Detailed Tele-Storke Cases:
Patient A:
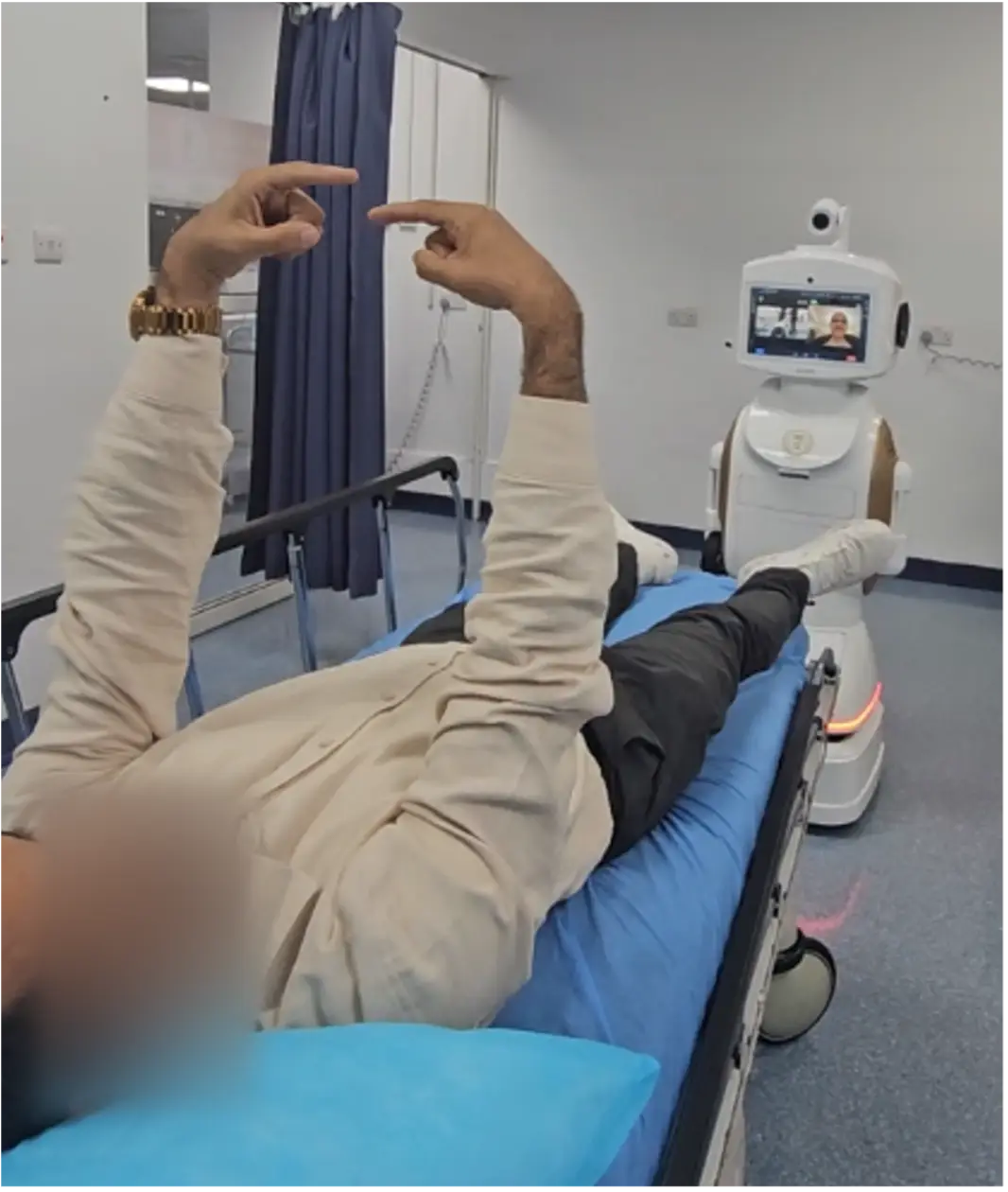
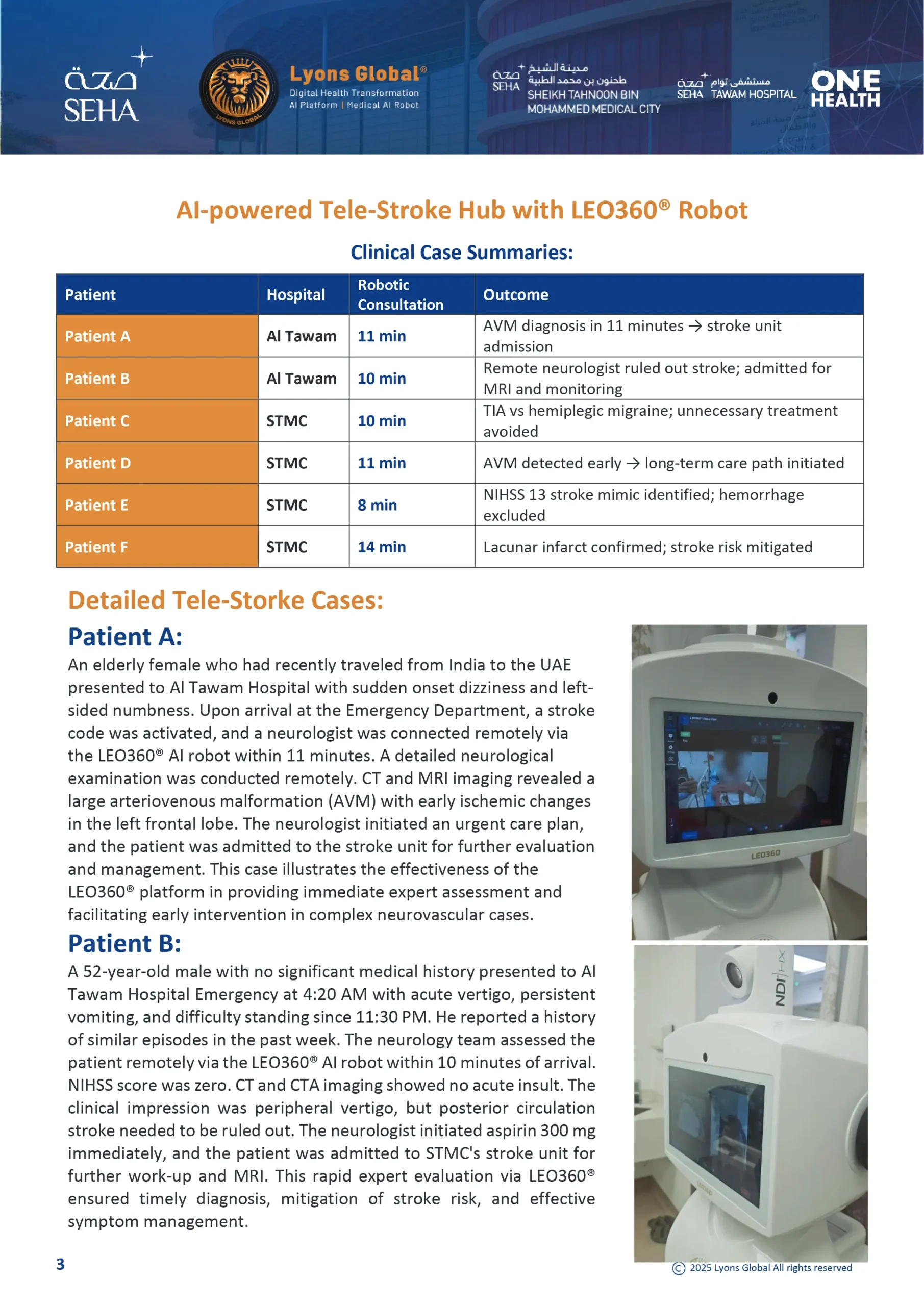
 An elderly female who had recently traveled from India to the UAE presented to Al Tawam Hospital with sudden onset dizziness and left-sided numbness. Upon arrival at the Emergency Department, a stroke code was activated, and a neurologist was connected remotely via the LEO360® AI robot within 11 minutes. A detailed neurological examination was conducted remotely. CT and MRI imaging revealed a large arteriovenous malformation (AVM) with early ischemic changes in the left frontal lobe. The neurologist initiated an urgent care plan, and the patient was admitted to the stroke unit for further evaluation and management. This case illustrates the effectiveness of the LEO360® platform in providing immediate expert assessment and facilitating early intervention in complex neurovascular cases.
An elderly female who had recently traveled from India to the UAE presented to Al Tawam Hospital with sudden onset dizziness and left-sided numbness. Upon arrival at the Emergency Department, a stroke code was activated, and a neurologist was connected remotely via the LEO360® AI robot within 11 minutes. A detailed neurological examination was conducted remotely. CT and MRI imaging revealed a large arteriovenous malformation (AVM) with early ischemic changes in the left frontal lobe. The neurologist initiated an urgent care plan, and the patient was admitted to the stroke unit for further evaluation and management. This case illustrates the effectiveness of the LEO360® platform in providing immediate expert assessment and facilitating early intervention in complex neurovascular cases.
A 52-year-old male  with no significant medical history presented to Al Tawam Hospital Emergency at 4:20 AM with acute vertigo, persistent vomiting, and difficulty standing since 11:30 PM. He reported a history of similar episodes in the past week. The neurology team assessed the patient remotely via the LEO360® AI robot within 10 minutes of arrival. NIHSS score was zero. CT and CTA imaging showed no acute insult. The clinical impression was peripheral vertigo, but posterior circulation stroke needed to be ruled out. The neurologist initiated aspirin 300 mg immediately, and the patient was admitted to STMC’s stroke unit for further work-up and MRI. This rapid expert evaluation via LEO360® ensured timely diagnosis, mitigation of stroke risk, and effective symptom management.
with no significant medical history presented to Al Tawam Hospital Emergency at 4:20 AM with acute vertigo, persistent vomiting, and difficulty standing since 11:30 PM. He reported a history of similar episodes in the past week. The neurology team assessed the patient remotely via the LEO360® AI robot within 10 minutes of arrival. NIHSS score was zero. CT and CTA imaging showed no acute insult. The clinical impression was peripheral vertigo, but posterior circulation stroke needed to be ruled out. The neurologist initiated aspirin 300 mg immediately, and the patient was admitted to STMC’s stroke unit for further work-up and MRI. This rapid expert evaluation via LEO360® ensured timely diagnosis, mitigation of stroke risk, and effective symptom management.
Patient C:
 A 36-year-old male presented to STMC with acute onset severe occipital headache, left arm numbness and weakness, vomiting, and blurred vision. The stroke code was activated at 10:14 PM. The neurologist remotely assessed the patient via LEO360® AI robot. Neurologic exam was notable for a mild hand drift but otherwise intact strength and function. NIHSS was 0. CT and CTA were unremarkable for hemorrhage or infarction. MRI confirmed no acute stroke, and the final diagnosis was a possible hemiplegic migraine versus TIA. An incidental azygos fissure was noted on chest CT. The patient was managed conservatively with aspirin, atorvastatin, and migraine medications. LEO360® enabled a rapid and accurate diagnosis, avoiding unnecessary intervention and enabling safe discharge with follow-up in the stroke clinic.
A 36-year-old male presented to STMC with acute onset severe occipital headache, left arm numbness and weakness, vomiting, and blurred vision. The stroke code was activated at 10:14 PM. The neurologist remotely assessed the patient via LEO360® AI robot. Neurologic exam was notable for a mild hand drift but otherwise intact strength and function. NIHSS was 0. CT and CTA were unremarkable for hemorrhage or infarction. MRI confirmed no acute stroke, and the final diagnosis was a possible hemiplegic migraine versus TIA. An incidental azygos fissure was noted on chest CT. The patient was managed conservatively with aspirin, atorvastatin, and migraine medications. LEO360® enabled a rapid and accurate diagnosis, avoiding unnecessary intervention and enabling safe discharge with follow-up in the stroke clinic.
Patient D:
 A 66-year-old male with a known history of hypertension, diabetes mellitus, and dyslipidemia presented to STMC with sudden onset of left-sided weakness while in his car. Stroke code was activated at 06:38 PM. Upon arrival to the ED, the patient was awake, responsive, with intact speech and no facial droop. Coordination testing revealed left-sided overshoot, and pronator drift was present. NIHSS score was 4. The LEO360® AI robot enabled remote evaluation by a neurologist within 11 minutes. Imaging revealed a large arteriovenous malformation (AVM) in the left frontal lobe, confirmed by MRA. No evidence of acute hemorrhage or infarction was found. The patient was admitted for stroke unit monitoring and further evaluation. Early identification of the AVM and appropriate triage through LEO360® prevented deterioration and avoided misdiagnosis, enabling targeted long-term management.
A 66-year-old male with a known history of hypertension, diabetes mellitus, and dyslipidemia presented to STMC with sudden onset of left-sided weakness while in his car. Stroke code was activated at 06:38 PM. Upon arrival to the ED, the patient was awake, responsive, with intact speech and no facial droop. Coordination testing revealed left-sided overshoot, and pronator drift was present. NIHSS score was 4. The LEO360® AI robot enabled remote evaluation by a neurologist within 11 minutes. Imaging revealed a large arteriovenous malformation (AVM) in the left frontal lobe, confirmed by MRA. No evidence of acute hemorrhage or infarction was found. The patient was admitted for stroke unit monitoring and further evaluation. Early identification of the AVM and appropriate triage through LEO360® prevented deterioration and avoided misdiagnosis, enabling targeted long-term management.
Patient E:
 A 62-year-old male with no known past medical history, recently arrived from Bangladesh, was found confused in his room at 4 PM after last being seen normal at 10 AM. He had contacted a friend earlier in the day reporting dizziness. Upon arrival to the ED, he was confused, aphasic, and showed right facial droop with NIHSS score of 13. The stroke code was activated at 07:24 PM. Using the LEO360® AI robot, the neurologist performed an immediate remote evaluation. Imaging showed no acute hemorrhage or major vessel occlusion. The patient was managed as a large vessel stroke mimic or evolving event, with further observation and supportive care. LEO360® enabled rapid stroke assessment, timely exclusion of hemorrhagic stroke, and expedited admission to the stroke unit for continued monitoring and treatment.
A 62-year-old male with no known past medical history, recently arrived from Bangladesh, was found confused in his room at 4 PM after last being seen normal at 10 AM. He had contacted a friend earlier in the day reporting dizziness. Upon arrival to the ED, he was confused, aphasic, and showed right facial droop with NIHSS score of 13. The stroke code was activated at 07:24 PM. Using the LEO360® AI robot, the neurologist performed an immediate remote evaluation. Imaging showed no acute hemorrhage or major vessel occlusion. The patient was managed as a large vessel stroke mimic or evolving event, with further observation and supportive care. LEO360® enabled rapid stroke assessment, timely exclusion of hemorrhagic stroke, and expedited admission to the stroke unit for continued monitoring and treatment.
Patient F:
 A 48-year-old male with hypertension and diabetes mellitus, non-compliant with medications, presented with left facial drift first noticed upon waking at 7 AM. He continued working despite the symptom, and later sought care at a clinic where he was found to be hypertensive (BP 190/100). He was referred to the emergency department. The stroke code was activated at 04:01 PM. The patient was alert, hemodynamically stable, and exhibited left facial drift with no limb weakness, aphasia, or visual field defects. CT head revealed a left frontal parafalcine focal hypodensity consistent with a likely lacunar infarct and suspected small partial filling defects of the superior sagittal sinus. Using the LEO360® AI robot, a neurologist remotely assessed the patient and confirmed a diagnosis of minor stroke. The patient was managed conservatively and admitted for observation and further secondary stroke prevention.
A 48-year-old male with hypertension and diabetes mellitus, non-compliant with medications, presented with left facial drift first noticed upon waking at 7 AM. He continued working despite the symptom, and later sought care at a clinic where he was found to be hypertensive (BP 190/100). He was referred to the emergency department. The stroke code was activated at 04:01 PM. The patient was alert, hemodynamically stable, and exhibited left facial drift with no limb weakness, aphasia, or visual field defects. CT head revealed a left frontal parafalcine focal hypodensity consistent with a likely lacunar infarct and suspected small partial filling defects of the superior sagittal sinus. Using the LEO360® AI robot, a neurologist remotely assessed the patient and confirmed a diagnosis of minor stroke. The patient was managed conservatively and admitted for observation and further secondary stroke prevention.Clinical Outcome Impact
|
Metric |
Before LEO360® |
With LEO360® |
Improvement |
|
Average Neurologist Response Time |
>120 minutes |
11.3 minutes |
>90% faster |
|
Unnecessary Transfers |
~3 per week |
<1 per week |
~80% reduction |
|
Diagnostic Accuracy |
Moderate |
Immediate & Confirmed on-site |
100% remote accuracy |
|
Time to Imaging Review |
~2 hours |
<15 minutes |
~85% faster |
Patients & Physicians Satisfaction
Key Enablers of Success
- Remote Neurologist Consultations
- AI-Enhanced Real-Time Video Assessment: Enabled precision NIHSS scoring and facial/limb observation.
- PACS Imaging Integration: Instant viewing of CT, CTA, and MRI results.
- Seamless EMR Access: Full digital handoff within the SEHA network.
- Secure Remote Access: Fully encrypted sessions over cloud-secured infrastructure.
Strategic Value for Health Systems
- Scalable Model: Adaptable for Cardiology, Behavioral Health, ICU, and Outpatient Consults.
- Geographical Equity: Eliminates gaps between rural and urban neurological care.
- Economic Efficiency: Reduces costs from unnecessary transport and inpatient days.
- Physician Empowerment: Empowers ER doctors, increases neurologist reach 10x.
Conclusion: A Blueprint for AI-Driven Stroke Excellence
The SEHA-LEO360® partnership sets a new gold standard for robotic stroke care. It proves that AI and robotics can not only support but amplify physician expertise in critical situations. This model is now replicable across the Middle East and globally.
“With LEO360®, every minute counts—and every minute saved saves lives.”
Acknowledgements:
SEHA Leadership: Saeed Kuwaiti, Dr. Badeya Al Bandar
STMC & Al Tawam Executive Team: Eisa Jaber Al Kuwaiti
Partners: Mohammed Aljaberi, Jassim Al-Khori
Authors:
- Lead Clinical Team:
Dr. Ali Hassan, Consultant Physician, Neurology Medical Clinic-MENUNC (Dep) Medical Affairs;
Dr. Tiago Moreira, Consultant Neurologist;
Dr. Ahmed Mahmoud Elsayed Hassan, Consultant Neurologist;
Dr. Ahmed Samir, Neurologist;
Dr. Sidra Aurangzeb, Consultant Neurologist;
Dr. Asmaa Sabbah, Consultant Neurologist;
- Emergency & Deployment Leadership:
Dr. Thiagarajan Jaiganesh, Chair & Consultant Emergency Physician, STMC Hospital (UAE)
Al Hamdi Obaid Ali Al Shamsi, Senior Manager – AI & Robotics, OneHealth (UAE)
- Innovation Strategy:
Bita Lyons, MBA-HLA
Keyvan Zeynali, MBA